Understanding the Fundamentals: What Hormones Are Released During Breastfeeding
Introduction
Breastfeeding is a beautiful and crucial part of motherhood, influenced by an intricate rhythm of hormonal actions and interactions. It not only provides infants with essential nutrients but also serves as a foundation for a strong mother-infant bond. But, do you know what hormones act behind the scenes? This article uncovers the key hormones involved in the breastfeeding journey, their function, how they foster mother-infant bonding and provide tips for managing hormonal fluctuations during and post breastfeeding. Let's unravel the hormone-driven world of breastfeeding.
What Are the Primary Hormones Involved in Breastfeeding?
Dissecting the Function of Prolactin
Revealing the Importance of Oxytocin
Fundamentally, two hormones dictate the course of breastfeeding: Prolactin and Oxytocin.
• Prolactin: This hormone, originating from the anterior pituitary gland, holds the title of 'milk producer.' It stimulates the mammary glands in a mother's breasts to produce milk, earning its name from the Latin word 'pro-lactin' or 'for milk.' The continual suckling of the baby contributes to its release, meaning more prolactin is produced, which in turn leads to increased milk production. This hormone is primarily responsible for ensuring a nursing mother's milk supply doesn't deplete but instead continually adapts to meet her baby's nutritional needs.
• Oxytocin: Oxytocin, commonly called the 'love hormone,' plays a crucial dual role in breastfeeding. This hormone, produced in the hypothalamus and secreted during nursing, stimulates the contraction of the mammary glands, which then release the milk, a procedure termed 'let-down.' Besides, oxytocin also boosts bonding between mother and infant during breastfeeding, weaving an emotional connection that strengthens each time the baby nurses.
Each of these hormones functions uniquely but synergistically, driving the sequence of lactation, ensuring adequacy of milk supply while fostering a strong emotional bond between mother and baby.
How Do These Hormones Function in Lactation?
In the process of lactation, both prolactin and oxytocin play integral roles. Here's how they do so:
Prolactin's Role in Producing Milk
- Origin: Prolactin is generated in the anterior pituitary gland.
- Function: Often referred to as the 'milk-producing hormone', it triggers the breast's mammary glands to produce milk.
- Relationship to Suckling: The level of prolactin released is directly proportional to the baby's nursing. The more the baby suckles, the higher the prolactin levels, thus, increasing the milk production.
- Prolactin and Mother's Milk Supply: High prolactin levels, especially post-childbirth, ensure a consistent milk supply for the newborn.
Oxytocin’s Influence in the Breastfeeding Process
- Origin: Oxytocin is produced in the hypothalamus.
- Role in Milk Release: Oxytocin is largely responsible for the 'milk let-down' process. It stimulates the contraction of the mammary glands, ejecting milk through the nipples.
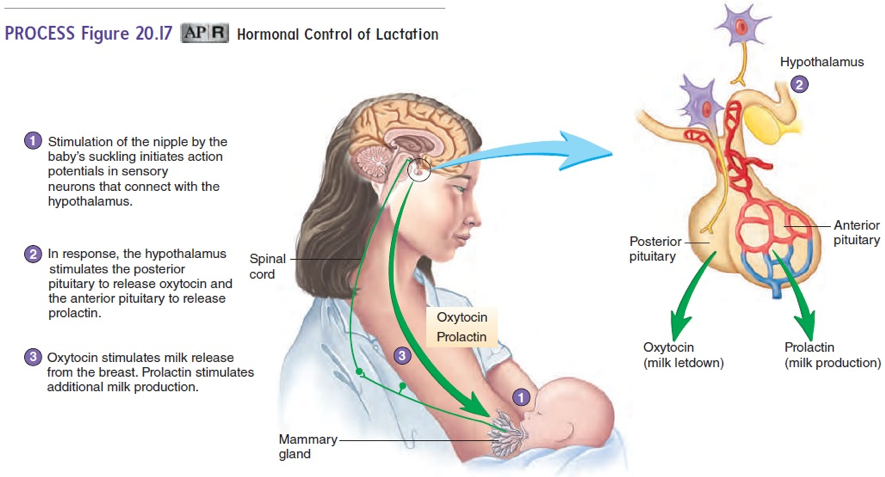
- Oxytocin and Emotional Bonding: Besides its physical function, oxytocin plays a significant psychological role. Named the 'love hormone,' it fosters an emotional bond between the mother and infant during breastfeeding.
In sum, the lactation process is a complex interplay of hormonal actions. Understanding this physiology of breast milk production can help new mothers adapt faster and better to their breastfeeding journey.
What Other Hormones Are Involved in the Breastfeeding Journey?
Yes, besides Prolactin and Oxytocin, the breastfeeding journey is also influenced by a complex network of other hormones. Each of these hormones plays a critical role in different stages of lactation, from pregnancy to weaning.
Here is a brief overview of some other hormones that orchestrate the breastfeeding process:
- Estrogen: Primarily associated with the female reproductive system, Estrogen plays a dual role during breastfeeding. Leading up to delivery, it stimulates the growth of the mammary glands. However, breastfeeding mothers generally have low estrogen levels, as high levels can interfere with milk production.
- Progesterone: This hormone complements estrogen by aiding in the development of milk-producing cells during pregnancy. Yet, similar to estrogen, successful breastfeeding requires lower progesterone levels post-delivery.
- Human Placental Lactogen (hPL): Produced by the placenta during pregnancy, hPL prepares the breasts for lactation by promoting the growth of ductal cells.
- Endorphins: These naturally occurring opiates can produce a feeling of tranquillity and promote bonding between the breastfeeding mother and infant.
Hence, while Prolactin and Oxytocin may be the stars of the show, a cast of other hormones are working behind the scenes throughout the breastfeeding journey, ensuring a seamless and fruitful lactation process.
How Do Hormones Foster Mother-Infant Bonding During Breastfeeding?
In the context of breastfeeding, hormones play an essential role in fostering a strong emotional connection between the mother and her newborn. Here's how:
1. Oxytocin’s Role in Bonding: Often regarded as the ‘love hormone,’ oxytocin is released during skin-to-skin contact and breastfeeding. This hormone significantly aids in establishing a solid emotional link between the mother and the infant. It induces feelings of peace, relaxation, and warmth, thus naturally encouraging the bonding process.
2. Prolactin and its Influence: Prolactin, also called the 'mothering hormone,' promotes the mother’s caregiving behavior. When the baby feeds, and the mother’s body generates milk, her prolactin levels increase. This boost in hormone production amplifies maternal instincts, further improving the mother-infant bond.
3. Hormonal Impact on Baby: Interestingly, not only do these hormones affect the mother, but they also impact the baby. Oxytocin, released during breastfeeding, enables the baby to feel secure and loved. It acts as a catalyst, facilitating the attachment process.
In summary, breastfeeding serves as a beautiful platform for both the mother and infant to establish a heartfelt bond. Key hormones like oxytocin and prolactin play pivotal roles in orchestrating this sublime interplay of emotions, proving once again the breathtaking complexity and wonder of the human body. As we delve more profoundly into the science of breastfeeding, it becomes increasingly clear that it is not merely a physiological process but also a hallmark of profound emotional exchange.
What Are the Tips for Managing Hormones Fluctuations During and Post Breastfeeding?
Navigating fluctuating hormones postpartum, especially in relation to breastfeeding, can be challenging for many new mothers. Understanding what's happening and having effective strategies can help manage these fluctuations better. Here are a few tips:
1. Understand and Anticipate Changes: It's crucial to understand that hormonal changes will occur during and after breastfeeding. The body is in constant adjustment to new needs and demands. Expecting these changes can help you prepare better.
2. Maintain a Healthy Diet: The right diet plays a vital role in hormone regulation. Ensure you consume plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Specific foods like salmon, spinach, eggs, almonds, and millet are rich in nutrients helpful in hormonal balance.
3. Stay Hydrated: Regular water intake is crucial for overall health, including hormone production. Water helps in maintaining the body's fluid balance, which is essential when breastfeeding.
4. Regular Exercise: Physical activity can aid in managing hormonal fluctuations. It doesn't necessarily mean intense workouts. Mild forms like yoga and stretching exercises can make a significant difference.
5. Take Rest: Good rest and sleep have a positive impact on hormone regulation. They can lower stress hormone levels, helping to maintain better equilibrium.
6. Keep Stress at Bay: Chronic stress interferes with hormone balance. Mindful practices such as meditation, mindfulness, and deep-breathing exercises can help manage stress levels.
7. Consult Healthcare Professionals: If hormonal fluctuations become unmanageable or lead to mood swings, depression, or anxiety, don't hesitate to seek help from healthcare professionals. They can provide guidance and possibly medication to help restore hormonal balance.
8. Stay Consistent with Breastfeeding: Maintaining a consistent breastfeeding schedule helps regulate hormones. The more the baby nurses, the higher the level of prolactin in the body, which aids in maintaining the milk supply.
Remember, every woman's experience is distinct and what works for one may not work for another. It's always important to listen to your body and do what feels most comfortable and beneficial for you.
Conclusion
Oxytocin plays a dual role in breastfeeding. Its primary function is to stimulate the contraction of the myoepithelial cells surrounding the milk-filled alveoli, thereby ejecting the milk through the nipples. Secondly, it aids in reinforcing the emotional bond between the mother and infant—making breastfeeding a unifying experience for both.
Related FAQs about what hormones are released during breastfeeding
What role does the hormone prolactin have in the breastfeeding process?
Prolactin, a hormone produced by the anterior pituitary gland, stimulates the mammary glands to produce milk. When a baby suckles, more prolactin is released, leading to increased milk production. Thus, prolactin ensures a steady milk supply that adapts to the baby's nutritional needs.
How does oxytocin contribute to mother-infant bonding during breastfeeding?
Oxytocin, often regarded as the 'love hormone,' is released during breastfeeding, fostering an emotional bond between mother and baby. This hormone induces feelings of peace, warmth, and relaxation, enhancing the bonding process. It also makes the baby feel secure, facilitating attachment.
How can a nursing mother manage hormonal fluctuations effectively during and post breastfeeding?
Managing hormonal fluctuations involves understanding the changes, maintaining a healthy diet, and staying hydrated. Regular exercise and rest, managing stress, and maintaining a consistent breastfeeding schedule also help. For severe fluctuations resulting in mood swings or anxiety, consultation with healthcare professionals is suggested.


