Unraveling Exclusive Breastfeeding: Insights Into What It Truly Means
Introduction
Exclusive breastfeeding is a term that is often used, but not always fully understood. This article seeks to unravel the meaning of exclusive breastfeeding, delve into its importance and discuss potential challenges faced by many mothers. It offers practical tips on overcoming these hurdles and also considers scenarios when supplementing may be needed. Ultimately, this guide aims to help mothers make informed decisions about their nursing journey.
What Does Exclusive Breastfeeding Mean?
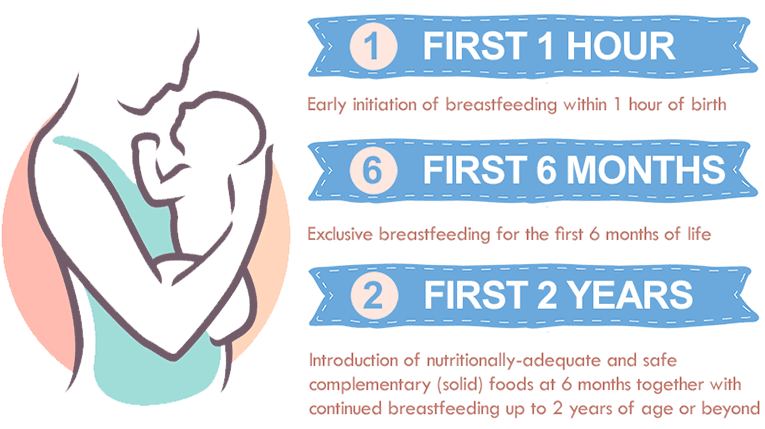
Exclusive breastfeeding refers to a specific feeding practice recommended by global health entities such as the World Health Organization (WHO). This practice holds importance in the first six months following a child's birth. To delve deeper:
1. Sole Source of Nutrition: Exclusive breastfeeding implies that an infant only receives breast milk, without any other food or drink, not even water during the first six months.
2. Vitamins, Drops/Syrups, and Medicines: These can be few exceptions to the exclusivity of breastfeeding, with the administration of certain vitamins, mineral drops/syrups, and medicines permitted. Oral rehydration solution is also acceptable.
3. Exclusivity: The term 'exclusive' means that the mother's milk is the ultimate source of nutrition for the infant. No other form of sustenance is provided.
4. Beyond Six Months: After the initial six-month period, weaning foods should be introduced alongside breast milk. However, the WHO recommends continuing breastfeeding until the child is two years or more.
Understanding these details helps us grasp the importance of exclusive breastfeeding for an infant's initial nutritional needs and overall growth and development.
Why is Exclusive Breastfeeding Crucial for Newborns?
The first six months of an infant's life are known for rapid growth and development. It's during this crucial period that exclusive breastfeeding plays a transformative role in a newborn's overall health and development. Here's why:
1. Optimal Nutrition: Human breast milk contains an ideal balance of nutrients that a baby needs for development. From proteins, carbohydrates to fats, breast milk has it all. It's a baby's comprehensive nutritional package.
2. Immunity Boost: Breast milk carries natural antibodies that contribute to developing a robust immune system in the newborn. These antibodies aid in fighting bacteria and viruses, providing immunological protection.
3. Gut Health: Exclusive breastfeeding aids in the proper development of the baby's digestive system. It helps in establishing a healthy gut microbiome, which is fundamental for immune function and nutrient absorption.

4. Emotional Bonding: The act of breastfeeding creates a deep emotional connection between the mother and the child. This bond plays a significant role in the baby's emotional development.
5. Healthy Growth Trajectory: A study by The Lancet affirms that children who were exclusively breastfed for six months experienced fewer infections, had a lower risk of mortality, and showed a better growth trajectory compared to non-breastfed children.
In conclusion, exclusive breastfeeding serves as the cornerstone for a child's healthy growth and development. It benefits not only their physical health but also contributes positively to their emotional well-being, setting a strong foundation for their future health.
What Are the Benefits of Being Exclusively Breastfed?
Exclusive breastfeeding brings with it a wealth of benefits that contribute synergistically to optimal infant health and development. These benefits are not merely confined to the early months of life but have far-reaching impacts extending well into adulthood. Here is a detailed break-down:
1. Preventing Ailments: Infants who are exclusively breastfed witness a substantial reduction in their susceptibility to a host of health issues. This includes reduced risks of developing diseases such as diarrhea, respiratory infections, and even sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).
2. Boosting Gut Health: Another remarkable benefit of exclusive breastfeeding lies in its role in shaping a robust and diverse gut flora in infants. This microbial community plays a key role in developing and fortifying the infant's immune system.
3. Meeting Nutritional Requirements: Breast milk is the perfect blend of all vital nutrients tailored to meet the unique needs of the newborn at each stage of its early development. The mix of proteins, carbohydrates, fats, and antibodies adjusts itself as the baby grows, ensuring optimal nutrition.
4. Strengthening Emotional Connectivity: Beyond the physical benefits, breastfeeding also supports emotional and psychological well-being. The intimate interaction promotes a powerful mother-child bond, which is essential for the infant's emotional and mental development.
According to the World Health Organization, an estimated 820,000, or 13.8% of all deaths worldwide in children under five, could be prevented each year with increased breastfeeding. Thus the value of exclusive breastfeeding is immeasurable, contributing to a healthier and brighter future for the child.
How Can Mothers Overcome Challenges with Exclusive Breastfeeding?
While exclusive breastfeeding comes with a multitude of benefits, it's not without its challenges. However, these hurdles can be effectively managed with the correct strategies and ample support. Here's a breakdown of common challenges and ways to navigate them:
1. Latching Difficulties: This is a common issue many new mothers face. Trying different breastfeeding positions often helps. For example, the cradle hold or football hold can offer better control over the baby's head allowing the baby to latch on more easily.
2. Sore Nipples: This is a condition most, if not all, breastfeeding mothers go through. Using nipple creams or lanolin after each feed can provide relief. It can also be beneficial to allow your nipples to air dry and heal.
3. Low Milk Supply: This issue can cause a lot of stress and worry for mothers. To combat this, stay hydrated, include lactation-boosting foods in your diet, like oats and fennel, and nurse your baby often. Breastfeeding works on a supply-demand basis; the more your baby nurses, the more milk your body produces.
4. Breastfeeding Pain: Pain can result from wrong latching or an infection. Consulting a lactation expert can help diagnose and address the cause of this pain.
5. Societal Pressures: In an era where bottle-feeding is widely accepted, nursing can sometimes attract unwanted attention. You don't have to face this alone; seek support from your partner, family, friends, or breastfeeding support groups.
Lastly, remember that it's completely normal to face challenges in your breastfeeding journey. What's important is to stay informed, prepared and to know where to seek help when necessary.
When Might Supplemental Feeding Become Necessary During Exclusive Breastfeeding?
While exclusive breastfeeding is universally recommended, circumstances may arise where the inclusion of supplemental feeding becomes inevitable for a nursing mother and her infant. These scenarios are defined below:
- Insufficient Weight Gain in Infants: As an indicator of healthy growth, infants must gradually gain weight after birth. If significant weight gain is not observed, it might indicate that the infant is not receiving the required nutrients solely from breast milk, thus necessitating supplemental feeding.
- Low Milk Supply: Some nursing mothers may experience issues with producing sufficient breast milk. Factors such as maternal health, lifestyle behaviors, and breastfeeding technique can impact the milk supply. In such instances, supplements might be introduced to ensure the baby’s nutritional needs are met.
- Premature Birth: Premature babies often have specific nutritional needs and may require additional supplements to achieve healthy growth and development.
- Maternal Health: There might be instances where the mother is unable to breastfeed due to health issues or medical treatments. Thus, supplements become necessary to provide the infant with critical nutrients.
The key takeaway here is that each breastfeeding journey is unique and supplemental feeding might be needed in certain circumstances. However, it's crucial to involve healthcare professionals in these situations for guidance. Furthermore, introducing supplements should not be seen as a transition away from breastfeeding. Rather, their role should be perceived as complementary, still preserving the benefits of breast milk while ensuring necessary nutritional care for the infant.
Conclusion
Exclusive breastfeeding offers numerous benefits for infants, but it can also pose challenges for some mothers. Despite the issues, many of them can be addressed with the proper guidance, support system, and resources. Always consult health professionals for personalised advice.
Related FAQs about what does exclusively breastfed mean
Does exclusive breastfeeding also exclude water and other liquids?
Yes, exclusive breastfeeding means that the infant receives only breast milk for the first six months of life. This includes exclusion of water, tea, juice, formula, and any other liquids or solid food, except for vitamins, medicine or nutritional supplements as advised by a healthcare professional.
What are some common hurdles when exclusively breastfeeding and how can they be addressed?
Common hurdles include issues with latching, sore nipples, low milk supply, and societal pressures. They can be addressed through lactation consultation, using nipple creams, promoting more frequent nursing sessions, maintaining a nutritious diet, and seeking emotional support from family, friends or support groups.
When would it be necessary to introduce supplemental feeding during exclusive breastfeeding?
Supplemental feeding might be required if the infant isn't gaining sufficient weight, the mother isn't producing enough milk, or in case of premature birth. It's also necessary if the mother is not able to breastfeed due to health issues or medical treatments. Always consult a healthcare professional for advice.


